- Joined
- Jun 11, 2025
- Messages
- 5
- Thread Author
- #1
In 2000, around 14 million people died from cardiovascular diseases globally, while in 2019, close to 18 million died.
The percentage of deaths from cardiovascular diseases is growing faster than the global population, and in developed countries, this rate continues to rise, both due to a decrease in deaths from other causes and other factors.
Athletes have a lower overall mortality rate, but a higher percentage of deaths from cardiovascular diseases. In sports medicine, there’s a term called Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD), which is the leading cause of death in athletes, often caused by undiagnosed heart conditions. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and congenital coronary artery anomalies are frequent causes even in younger athletes [1] [2]
And most common reason is exacerbation of existing but hidden cardiovascular pathologies, which, according to doctors, did not pose a danger previously, or SCD.
The general recommendation of doctors today is to check not only blood pressure and lipid profile. If you have ever looked at the blood tests required for athletes, women, vegans, and older people both, you have probably noticed such an indicator as Homocysteine.
So what is Homocysteine and why it is so important?
Homocysteine(HCY) is a sulfhydryl-containing amino acid produced by the demethylation of methionine, important amino acid derived from all sources of protein.
All types of meat and dairy products are rich in methionine, an essential amino acid that plays a key role in protein synthesis and antioxidant defense. It is crucial for normal cellular function, growth, and development, and has significant implications for managing cancer and other diseases. However, homocysteine (HCY) is a side effect of its positive impact.
Elevated homocysteine level is risk factor for cardiovascular diseases:
It was proven by numerous studies that a high level of HCY is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary heart disease and stroke. [4][5][6]
So chance of having heart and blood vessel disease goes up severely if your homocysteine level is high. There is a relationship between high levels of homocysteine and artery damage. That can lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and blood clots.
All recent studies indicate that homocysteine levels directly affect the development of cardiovascular diseases and the homocysteine test is currently used as a very good index of cardiac disease severity [7]
According to various estimates, from 32 to 54% of athletes have elevated homocysteine, which defines them as a high-risk group. [9] [10]
The exercise itself is one factors that increases blood homocysteine levels, and elevated homocysteine levels cause oxidative stress.
In this study blood was collected before, 30 min after, and 90 min after exercise, and at the same time points under control conditions. Samples were analyzed for the homocysteine concentration and the plasma Hcy concentration was significantly increased at Post 30 min (+ 0.83 ± 0.70 µmol/L, P = 0.003) compared with that at Pre in the exercise condition.[11]
A similar study conducted on hockey and football players confirms these data.[12]
Recent studies show that homocysteine (Hcy) levels directly impact the development of cardiovascular diseases, and the Hcy test is now widely used to assess the severity of heart disease. The medical community has agreed that plasma homocysteine levels are an independent predictor of chronic inflammation and the risk of cardiac mortality.[13] [14]
High homocysteine levels are associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to vascular endothelial damage and atherosclerosis [16][17].
Homocysteine can induce systemic inflammation by increasing oxidative stress and activating inflammatory pathways. In RA patients, homocysteine levels are correlated with markers of inflammation such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and complement components C3 and C4 [18]
High homocysteine levels are an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. They contribute to endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation, all of which are critical in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis [19]
Elevated homocysteine levels are linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and arterial wall inflammation, further highlighting its role in systemic inflammatory processes [20]
Elevated homocysteine levels have been linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.[21] Individuals with high homocysteine levels are more likely to exhibit markers of Alzheimer’s progression in brain tissue, such as neurofibrillary tangles, accumulation of dysfunctional proteins (amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau), and brain atrophy. [22] According to one meta-analysis, each 5 µmol/L increase in homocysteine level is associated with a 15% increase in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.[23]
Elevated levels of homocysteine have been associated with many diseases, including:
Secondly, nature didn’t design us to be bodybuilders or powerlifters – these are very specific forms of strain. Research shows that cardio exercises have little to no effect or slightly reduce homocysteine levels, while high-intensity exercises (such as weightlifting, sprints, or boxing) can increase homocysteine levels. These studies were conducted without the use of steroids. [24] [25]
But when it comes to PEDs things becomes more severe.
As we already wrote above, 2021 became a record year for the number of deaths among bodybuilders and strength athletes.
Many of these recent fatalities were related to cardiovascular issues, highlighting the need to examine the impact of anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) and strength training on the cardiovascular system.
This surge in deaths has garnered significant attention within the bodybuilding community, though it has largely gone unnoticed in the medical field.
Many studies have reported that AAS use is linked to elevated blood pressure, a problem we’ve already addressed here with corresponding strategies.
However, numerous studies have also shown that AAS negatively affects other known cardiovascular disease risk factors. For instance, AAS has been proven to significantly increase homocysteine levels in bodybuilders . [26].
Another study shows that intake of anabolic steroids, as used typically by bodybuilders in the build-up phase, induces acute hyperhomocysteinemia and is likely to initiate an additional, potentially atherothrombotic mechanism in this group of athletes. [27]
Also recent research found that HCY levels were significantly higher in steroid users compared other people. [28]
Therefore, anyone who is not mentally prepared for a nandrolone-solo-deca-dick cycle should include Homocysteine in their blood tests and read next chapter to figure out what to do.
What to do ?
According to all existing doctor’s prescriptions, the only way to cope with an increase in homocysteine is to use methyl donors – methylated B vitamins as well as some other substances like TMG.
In this particular case nutritional supplements can give a head start to pharmaceutical drugs. Even in injection forms of pharmaceutical vitamins B, consists of the cheapest forms of vitamins with low digestibility are used – cyanocobolamin, which is divided into the poison cyanide and vitamin B12 in the liver, as well as folic acid, which has low bioavailability and in many people is not absorbed at all, but L-methylfolate, can achieve plasma folate levels up to 700% higher than synthetic folic acid, as well as Pyroxidine hydrochloride – vitamin B6, which is much inferior to Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate the active form of vitamin B6.
This claims are proven with a recent study, that shows that HCY levels were significantly higher in steroid users compared other people, even if vitamin B12 and folate levels, were at the same level, which suggests that bodybuilders and especially those using steroids require additional intake of B vitamins. [30]
Another study confirms that intakes of folate, vitamin B6 and B12 were associated with lower plasma HCY levels [31]
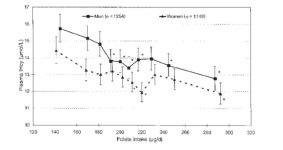
Thus, the graph assessed the dependence of homocysteine levels on folate intake (vitamin B9). As we can see, adequate intake of vitamin B really has a positive effect.[32]
Therefore, our new product, composed of the most top forms of vitamins B and substances, including their formations, helps you avoid systemic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases, improve nerve health and enhance protein synthesis in muscles and much more for the price of mint candy at the checkout!
Cardiovascular diseases develop slowly, but appear unexpectedly.
A little prevention today is a great investment for maintaining health for many years!
[1] https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.62.2.218
[2] https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199307013290113
[3]https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9885939/table/Tab1/?report=objectonly
[4] https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.54.4.599
[5] https://doi.org/10.1177/204748739900600408
[6] https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/ss/slideshow-visual-guide-to-heart-disease
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34816003/
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20087304/
[10] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17598967/
[11] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37062848/
[12] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21480058/
[13] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34816003/
[14] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34765237/
[15] Lazzerini, P., Selvi, E., Lorenzini, S., Capecchi, P., Ghittoni, R., Bisogno, S., Catenaccio, M., Marcolongo, R., Galeazzi, M., & Laghi-Pasini, F. (2006). Homocysteine enhances cytokine production in cultured synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.. Clinical and experimental rheumatology, 24 4, 387-93 .
[16] Biçer et al., 2016
[17] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17822365/
[18] Yang, X., Gao, F., & Liu, Y. (2015). Association of homocysteine with immunological-inflammatory and metabolic laboratory markers and factors in relation to hyperhomocysteinaemia in rheumatoid arthritis.. Clinical and experimental rheumatology, 33 6, 900-3 .
[19] Mccully, K. (2009). Chemical pathology of homocysteine. IV. Excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation.. Annals of clinical and laboratory science, 39 3, 219-32 .
[20] https://journals.lww.com/bloodcoagu...e_association_between_homocysteine_and.1.aspx
[21] Tinelli C, Di Pino A, Ficulle E, Marcelli S, Feligioni M. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a Risk Factor and Potential Nutraceutical Target for Certain Pathologies. Frontiers in nutrition. 2019;6:49.
[22] Smith AD, Refsum H, Bottiglieri T, et al. Homocysteine and Dementia: An International Consensus Statement. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(2):561-570.
[23] Zhou F, Chen S. Hyperhomocysteinemia and risk of incident cognitive outcomes: An updated dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;51:55-66.
[24] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14656035/
[25] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17555540/
[26] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9885939/#CR18
[27] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11173010/#:~:text=Conclusion%3A Our study shows that,in this group of athletes.
[28] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16488899/
[29] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_118.x
[30] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16488899/
[31] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15871861/
[32] https://www.researchgate.net/figure...-in-men-and-women-by-deciles-of_fig1_11955653
The percentage of deaths from cardiovascular diseases is growing faster than the global population, and in developed countries, this rate continues to rise, both due to a decrease in deaths from other causes and other factors.
Athletes have a lower overall mortality rate, but a higher percentage of deaths from cardiovascular diseases. In sports medicine, there’s a term called Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD), which is the leading cause of death in athletes, often caused by undiagnosed heart conditions. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and congenital coronary artery anomalies are frequent causes even in younger athletes [1] [2]
In 2021, more than twenty professional competitive bodybuilders and several retired bodybuilders under 60 years old unexpectedly passed away.[3]So cardiovascular diseases are the main risk of mortality among both athletes and ordinary people.
And most common reason is exacerbation of existing but hidden cardiovascular pathologies, which, according to doctors, did not pose a danger previously, or SCD.
The general recommendation of doctors today is to check not only blood pressure and lipid profile. If you have ever looked at the blood tests required for athletes, women, vegans, and older people both, you have probably noticed such an indicator as Homocysteine.
So what is Homocysteine and why it is so important?
Homocysteine(HCY) is a sulfhydryl-containing amino acid produced by the demethylation of methionine, important amino acid derived from all sources of protein.
All types of meat and dairy products are rich in methionine, an essential amino acid that plays a key role in protein synthesis and antioxidant defense. It is crucial for normal cellular function, growth, and development, and has significant implications for managing cancer and other diseases. However, homocysteine (HCY) is a side effect of its positive impact.
Elevated homocysteine level is risk factor for cardiovascular diseases:
It was proven by numerous studies that a high level of HCY is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary heart disease and stroke. [4][5][6]
So chance of having heart and blood vessel disease goes up severely if your homocysteine level is high. There is a relationship between high levels of homocysteine and artery damage. That can lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and blood clots.
All recent studies indicate that homocysteine levels directly affect the development of cardiovascular diseases and the homocysteine test is currently used as a very good index of cardiac disease severity [7]
According to various estimates, from 32 to 54% of athletes have elevated homocysteine, which defines them as a high-risk group. [9] [10]
The exercise itself is one factors that increases blood homocysteine levels, and elevated homocysteine levels cause oxidative stress.
In this study blood was collected before, 30 min after, and 90 min after exercise, and at the same time points under control conditions. Samples were analyzed for the homocysteine concentration and the plasma Hcy concentration was significantly increased at Post 30 min (+ 0.83 ± 0.70 µmol/L, P = 0.003) compared with that at Pre in the exercise condition.[11]
A similar study conducted on hockey and football players confirms these data.[12]
Recent studies show that homocysteine (Hcy) levels directly impact the development of cardiovascular diseases, and the Hcy test is now widely used to assess the severity of heart disease. The medical community has agreed that plasma homocysteine levels are an independent predictor of chronic inflammation and the risk of cardiac mortality.[13] [14]
Homocysteine is an independent predictor of chronic inflammatory status and cardiac mortality risk and from 32 to 54% of athletes have elevated homocysteine.
Joint damage and systemic inflammation
Hyperhomocysteinemia (elevated homocysteine levels in the blood) has been linked to joint damage and systemic inflammation, contributing to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and inflammatory disorders. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), high homocysteine levels can worsen joint inflammation by boosting cytokine production in synoviocytes, which leads to increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-8, contributing to joint damage.[15].High homocysteine levels are associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to vascular endothelial damage and atherosclerosis [16][17].
Homocysteine can induce systemic inflammation by increasing oxidative stress and activating inflammatory pathways. In RA patients, homocysteine levels are correlated with markers of inflammation such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and complement components C3 and C4 [18]
High homocysteine levels are an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. They contribute to endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation, all of which are critical in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis [19]
Elevated homocysteine levels are linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and arterial wall inflammation, further highlighting its role in systemic inflammatory processes [20]
Elevated homocysteine levels have been linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.[21] Individuals with high homocysteine levels are more likely to exhibit markers of Alzheimer’s progression in brain tissue, such as neurofibrillary tangles, accumulation of dysfunctional proteins (amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau), and brain atrophy. [22] According to one meta-analysis, each 5 µmol/L increase in homocysteine level is associated with a 15% increase in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.[23]
Elevated levels of homocysteine have been associated with many diseases, including:
- cardiovascular disease
- congestive heart failure
- stroke
- migraines
- age-related macular degeneration
- hearing loss
- brain atrophy
- Alzheimer disease
- systemic inflammation
- joint damage
CONCLUSION
Homocysteine, a recently discovered but crucial marker of overall health, plays a significant role in various diseases, including cardiovascular and inflammatory conditions. Its levels are closely linked to longevity and well-being. Given its impact on health, regular monitoring of homocysteine is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing potential risks.Homocysteine 2: Why are so many athletes falling victim to cardiovascular issues?
Firstly, the increased protein intake required as part of a sports diet leads to higher homocysteine levels because you consume more of the amino acid methionine overall.Secondly, nature didn’t design us to be bodybuilders or powerlifters – these are very specific forms of strain. Research shows that cardio exercises have little to no effect or slightly reduce homocysteine levels, while high-intensity exercises (such as weightlifting, sprints, or boxing) can increase homocysteine levels. These studies were conducted without the use of steroids. [24] [25]
But when it comes to PEDs things becomes more severe.
As we already wrote above, 2021 became a record year for the number of deaths among bodybuilders and strength athletes.
Many of these recent fatalities were related to cardiovascular issues, highlighting the need to examine the impact of anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) and strength training on the cardiovascular system.
This surge in deaths has garnered significant attention within the bodybuilding community, though it has largely gone unnoticed in the medical field.
Many studies have reported that AAS use is linked to elevated blood pressure, a problem we’ve already addressed here with corresponding strategies.
However, numerous studies have also shown that AAS negatively affects other known cardiovascular disease risk factors. For instance, AAS has been proven to significantly increase homocysteine levels in bodybuilders . [26].
Another study shows that intake of anabolic steroids, as used typically by bodybuilders in the build-up phase, induces acute hyperhomocysteinemia and is likely to initiate an additional, potentially atherothrombotic mechanism in this group of athletes. [27]
Also recent research found that HCY levels were significantly higher in steroid users compared other people. [28]
…the good news is that of all the steroids, only Nandrolone most likely does not raise homocysteine, which was indirectly confirmed by recent experience on rats [29]People on TRT and AAS users prone to have a high homocysteine levels and higher mortality risks.
Therefore, anyone who is not mentally prepared for a nandrolone-solo-deca-dick cycle should include Homocysteine in their blood tests and read next chapter to figure out what to do.
What to do ?
According to all existing doctor’s prescriptions, the only way to cope with an increase in homocysteine is to use methyl donors – methylated B vitamins as well as some other substances like TMG.
In this particular case nutritional supplements can give a head start to pharmaceutical drugs. Even in injection forms of pharmaceutical vitamins B, consists of the cheapest forms of vitamins with low digestibility are used – cyanocobolamin, which is divided into the poison cyanide and vitamin B12 in the liver, as well as folic acid, which has low bioavailability and in many people is not absorbed at all, but L-methylfolate, can achieve plasma folate levels up to 700% higher than synthetic folic acid, as well as Pyroxidine hydrochloride – vitamin B6, which is much inferior to Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate the active form of vitamin B6.
This claims are proven with a recent study, that shows that HCY levels were significantly higher in steroid users compared other people, even if vitamin B12 and folate levels, were at the same level, which suggests that bodybuilders and especially those using steroids require additional intake of B vitamins. [30]
Another study confirms that intakes of folate, vitamin B6 and B12 were associated with lower plasma HCY levels [31]

Thus, the graph assessed the dependence of homocysteine levels on folate intake (vitamin B9). As we can see, adequate intake of vitamin B really has a positive effect.[32]
Summary and Quick Facts for Homocysteine Reduction:
- Elevated homocysteine levels in the bloodstream have been linked with a wide range of severe health problems.
- A high-protein diet, especially one that includes red meat and dairy products, can increase blood levels of homocysteine.
- Strength and other types of high intensity training raise serum homocysteine levels.
- Bodybuilders, training athletes, senior people, vegans, people on TRT and other AAS users needs more B vitamins than average people in general.
- Supplementation with B-vitamins, including folate, vitamin B6 and B12 have been shown in numerous studies to help lower homocysteine levels.
- Betaine (TMG) and choline are also related to lower circulating homocysteine concentrations.
Therefore, our new product, composed of the most top forms of vitamins B and substances, including their formations, helps you avoid systemic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases, improve nerve health and enhance protein synthesis in muscles and much more for the price of mint candy at the checkout!
Cardiovascular diseases develop slowly, but appear unexpectedly.
A little prevention today is a great investment for maintaining health for many years!
[1] https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.62.2.218
[2] https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199307013290113
[3]https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9885939/table/Tab1/?report=objectonly
[4] https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.54.4.599
[5] https://doi.org/10.1177/204748739900600408
[6] https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/ss/slideshow-visual-guide-to-heart-disease
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34816003/
[9] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20087304/
[10] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17598967/
[11] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37062848/
[12] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21480058/
[13] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34816003/
[14] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34765237/
[15] Lazzerini, P., Selvi, E., Lorenzini, S., Capecchi, P., Ghittoni, R., Bisogno, S., Catenaccio, M., Marcolongo, R., Galeazzi, M., & Laghi-Pasini, F. (2006). Homocysteine enhances cytokine production in cultured synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.. Clinical and experimental rheumatology, 24 4, 387-93 .
[16] Biçer et al., 2016
[17] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17822365/
[18] Yang, X., Gao, F., & Liu, Y. (2015). Association of homocysteine with immunological-inflammatory and metabolic laboratory markers and factors in relation to hyperhomocysteinaemia in rheumatoid arthritis.. Clinical and experimental rheumatology, 33 6, 900-3 .
[19] Mccully, K. (2009). Chemical pathology of homocysteine. IV. Excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation.. Annals of clinical and laboratory science, 39 3, 219-32 .
[20] https://journals.lww.com/bloodcoagu...e_association_between_homocysteine_and.1.aspx
[21] Tinelli C, Di Pino A, Ficulle E, Marcelli S, Feligioni M. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a Risk Factor and Potential Nutraceutical Target for Certain Pathologies. Frontiers in nutrition. 2019;6:49.
[22] Smith AD, Refsum H, Bottiglieri T, et al. Homocysteine and Dementia: An International Consensus Statement. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(2):561-570.
[23] Zhou F, Chen S. Hyperhomocysteinemia and risk of incident cognitive outcomes: An updated dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;51:55-66.
[24] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14656035/
[25] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17555540/
[26] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9885939/#CR18
[27] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11173010/#:~:text=Conclusion%3A Our study shows that,in this group of athletes.
[28] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16488899/
[29] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_118.x
[30] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16488899/
[31] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15871861/
[32] https://www.researchgate.net/figure...-in-men-and-women-by-deciles-of_fig1_11955653